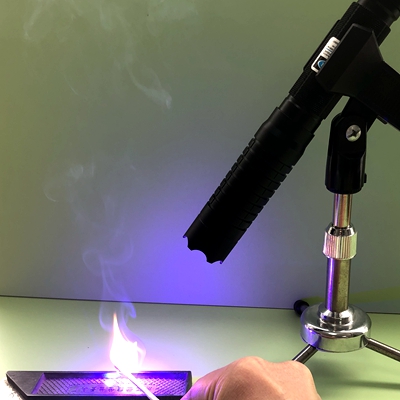
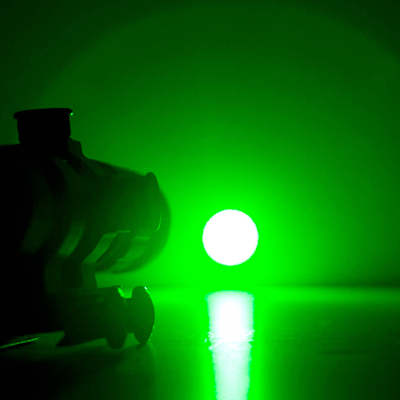
See Additional Content Below
beamqlaser@gmail.com | info@beamq.com Chat box at bottom
Featured Products
Real Output Power 5W 5000mW Blue Laser Torch Adjustable Focus Kaleidoscope
$259.00 $199.00Save: 23% off

High Power Green Laser Dazzler Non-lethal Dazzler Weapon Eye Safe 532nm Green Beam
$560.00 $369.00Save: 34% off

15W Blue Laser Torch Pointers Flashlight Highest Real 15,000mW Output Power
$498.00 $490.00Save: 2% off

Portable Laser Dazzler Law Enforcement and Self Defense High Power Lasers for Sale
$490.00 $490.00Save: 0% off

465nm Sky Blue Laser Pointers Torch Output Power 3W 3000mW Water Proof Burning
$599.00 $199.00Save: 67% off

Most Powerful 300-500mW Green Laser Rifle Sight Long Range Laser for AR15
$159.00 $129.00Save: 19% off
Monthly Specials For April
MID IR supercontinuum laser Light Source broadband white light source
$58,000.00 $55,000.00Save: 5% off
the White Laser 0.5W-20W RGB Red Green Blue 3 in 1 Color Laser Projector White Laser Source
$297.00 $199.00Save: 33% off
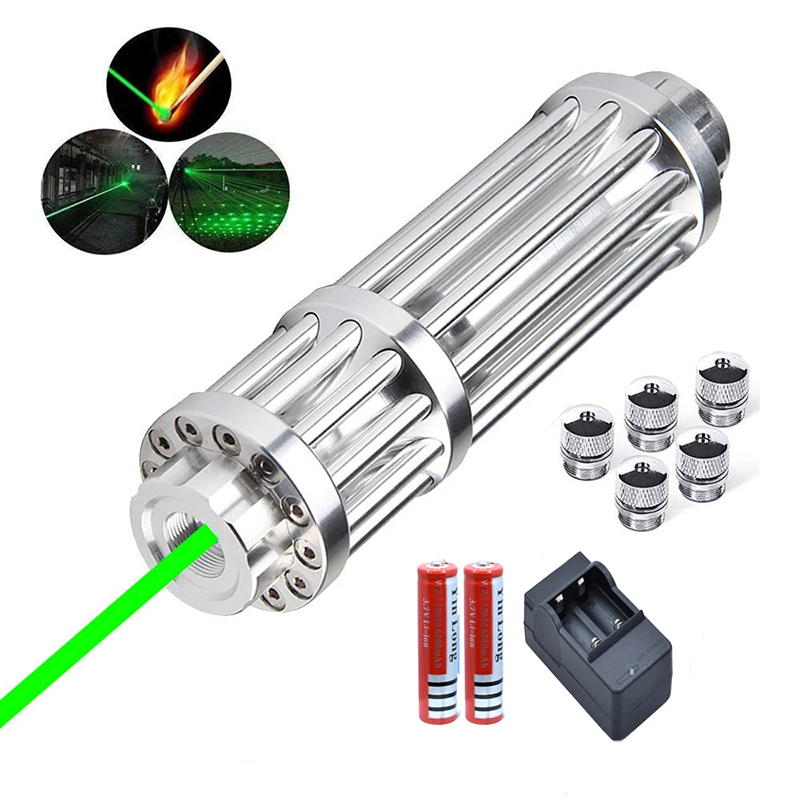

Laser Dazzler For Sale Green LightOutdoor Self-defense Expedition Rescue Signal Light Starry Laser Pointer
$80.00 $69.00Save: 14% off
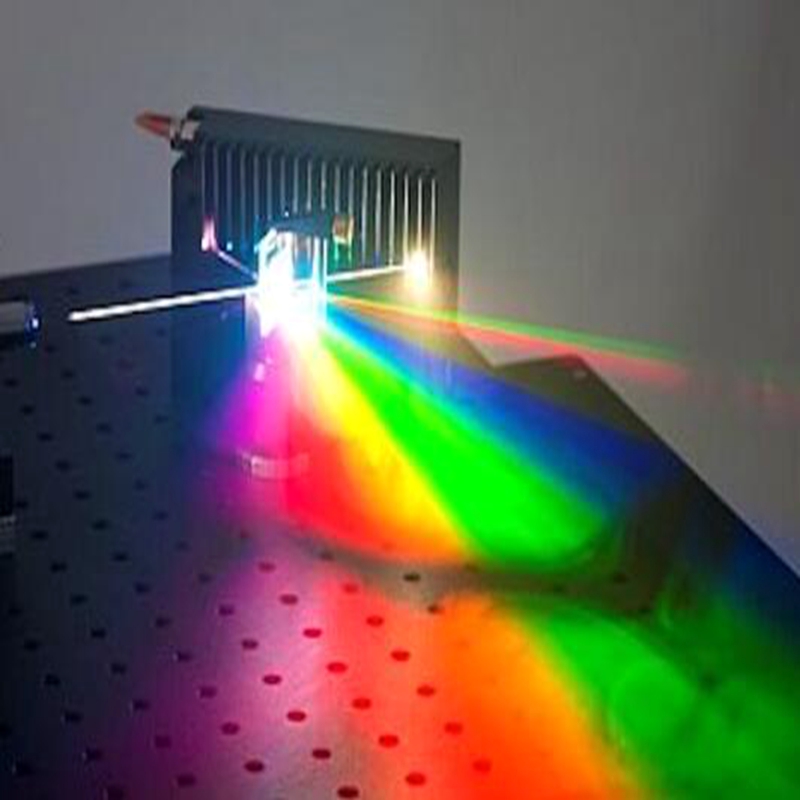

Supercontinuum Laser Source White Light Source 410nm-2400nm 7W Total Power PRO-MLD
$62,000.00 $58,000.00Save: 6% off